Turbidity Currents
During floods, the density of river water usually increases due to a subsequent increase in the concentration of the suspended sediment that the river carries, causing the river to plunge underneath the free surface of a receiving water basin and form a turbidity current that continues to flow along the bottom.
The study and understanding of such complex phenomena is of great importance, as they constitute one of the major mechanisms for suspended sediment transport from rivers into oceans, lakes or reservoirs. Unlike most of the previous numerical investigations on turbidity currents, in this project, a 3D numerical model that simulates the dynamics and flow structure of turbidity currents, through a multiphase flow approach is proposed, using the commercial CFD code FLUENT.
A series of numerical simulations that reproduce particular published laboratory flows are presented. The detailed qualitative and quantitative comparison of numerical with laboratory results indicates that apart from the global flow structure, the proposed numerical approach efficiently predicts various important aspects of turbidity current flows, such as the effect of suspended sediment mixture composition in the temporal and spatial evolution of the simulated currents, the interaction of turbidity currents with loose sediment bottom layers and the formation of internal hydraulic jumps.
Furthermore, various extreme cases among the numerical runs considered are further analyzed, in order to identify the importance of various controlling flow parameters.
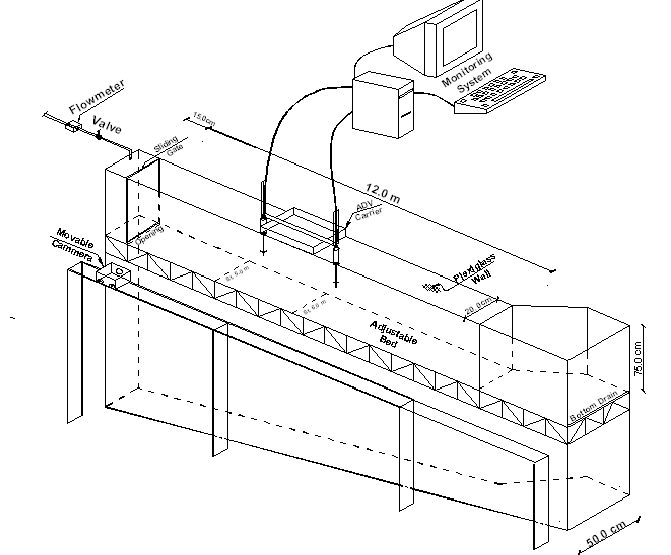
3D Laboratory Setup
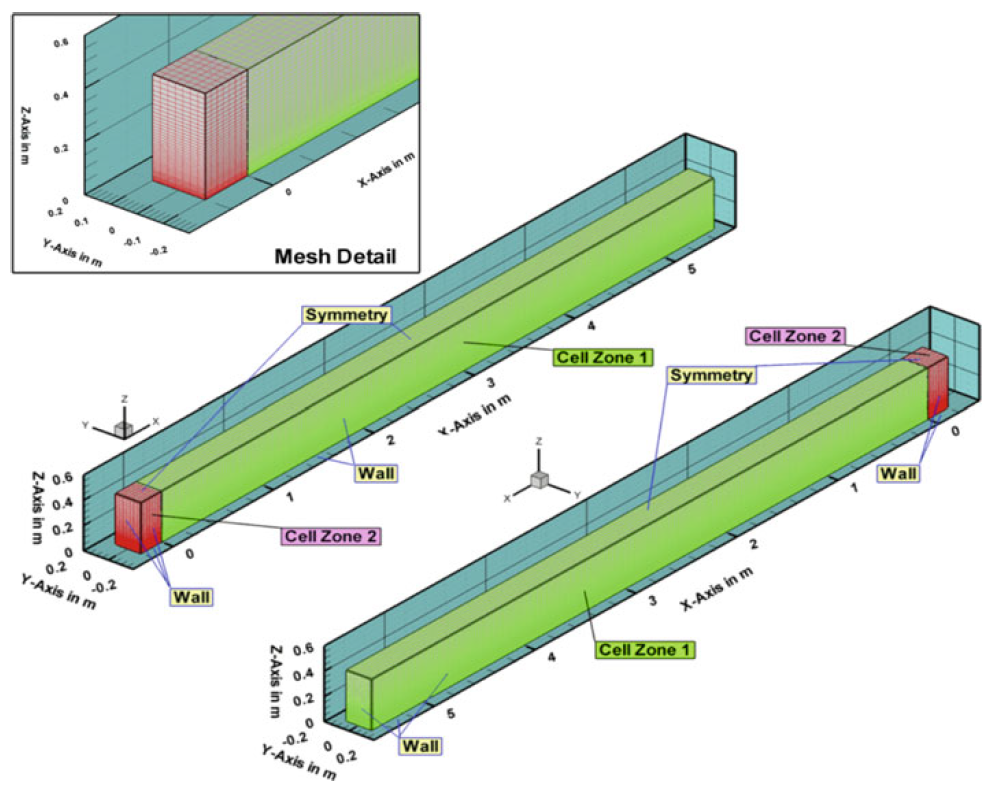
Geometry, mesh and boundary conditions used in the numerical simulations
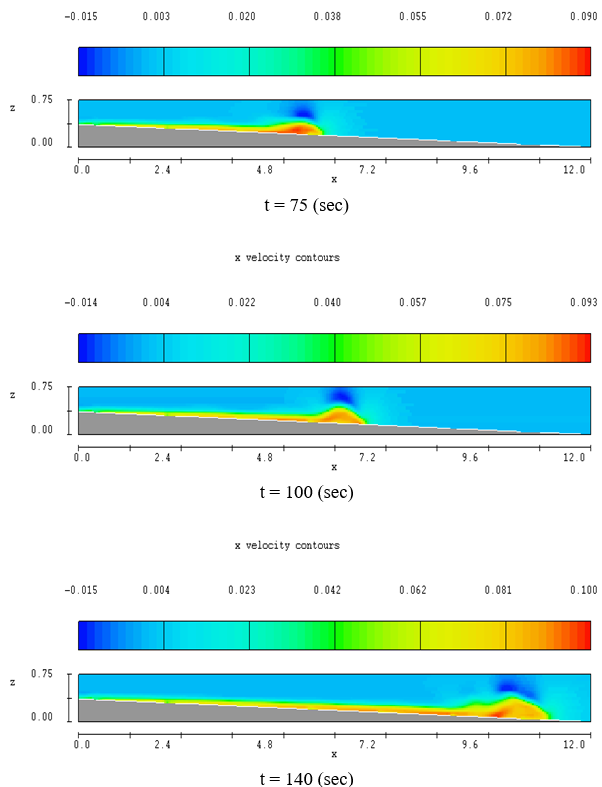
X Velocity Contours of Turbid Currents
This numerical project was conducted by XAV experts.
شبيه سازي عددي رفتار ديناميكي جريانهاي چگال با توجه به مدلهاي مختلف آشفتگي
شبيه سازي عددي رفتار ديناميکي و مشخصات هيدروليکي جريان چگال (حرکت پيشاني و بدنه و دنبالهاي از سيال سنگين به درون سيال سبکتر است و نيروي شناوري يا نيروي ثقل باعث ايجاد نيروي رانش ميشود)و نحوه تغييرات پروفيلهاي سرعت و غلظت به تغيير پارامترهاي اصلي و کنترل کننده از قبيل زاويه شيب کانال ، غلظت اوليه رسوب و دبي ورودي و عدد ریچاردسون ورودی
جريانهاي چگالي، جريانهاي ثقلي هستند كه اختلاف چگالي يا اختلاف وزن واحد حجم بين دو سيال بواسطه رسوبات معلق ميباشد. در اين تحقيق جريانهاي چگالي كه به عنوان عامل اصلي انتقال رسوبات به داخل مخازن سدها، درياها و اقيانوسها ميباشد، به كمك نرم افزار عددي فلوئنت شبيهسازي ميشود.
اين نرم افزار معادلات حاكم بر جريان را با استفاده از روش حجم محدود حل ميكند. . براي حل معادلات ناوير استوکس در حالت جريان آشفته از روش ميانگين گيري رينولدز(RANS) استفاده مي شود و براي حل تنش هاي رينولدز از رابطه بوزينسک استفاده خواهد شد. مدلهاي آشفتگي زيادي براي محاسبه لزجت آشفتگي اضافه شده در معادلات ميانگين گيري رينولدز وجود دارد مثل : مدل تنش رينولدزي (RSM) مدل استاندارد ، مدل (RNG) و مدلRealizable . پس از انتخاب مدل آشفتگي مناسب براي صحتسنجي نرمافزار در تعيين پارامترهاي هيدروليكي جريانهاي چگالي از جمله پروفيلهاي سرعت و غلظت، از يك نمونه آزمايشگاهي استفاده خواهد شد.
نتايج حاصل از شبيهسازي با اندازهگيريهاي آزمايشگاهي مربوط مقايسه می گردد لازم به ذکر است که براي مقايسه از آزمايشات انجام گرفته توسط حسيني و همكاران كه بر روی دستگاه آزمايش شامل کانالي به طول 12 متر و عرض 20 سانتيمتر و ارتفاع 75 سانتيمتر ميباشد، استفاده گرديد. پارامترهاي محاسبه شده شامل پروفيل سرعت و غلظت در بدنه و سري زماني سرعتهاي لحظهاي در بدنه و پيشاني جريان خواهند بود
شبيه سازي عددي در شيب کم انجام خواهد شد. بطور کلي نيز جريانهاي چگال در طبيعت عمدتاً در شيبهاي بسيار کم در کف درياها و اقيانوس ها بوجود مي آيند. لذا نيازي به انجام آزمايشات در شيبهايي بيش از 3 درصد احساس نميگردد. در انتها باید خاطرنشان نمود که جريان به صورت دو فاز ، شامل آب ساكن و فاز جريان چگال(غليظ) خواهد بود.


0 Comments