Pressure
The pressure could be measured by different devices such as barometer, piezometer and Pitot tube.
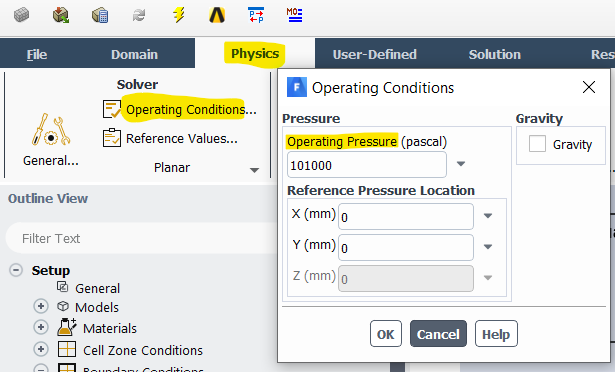
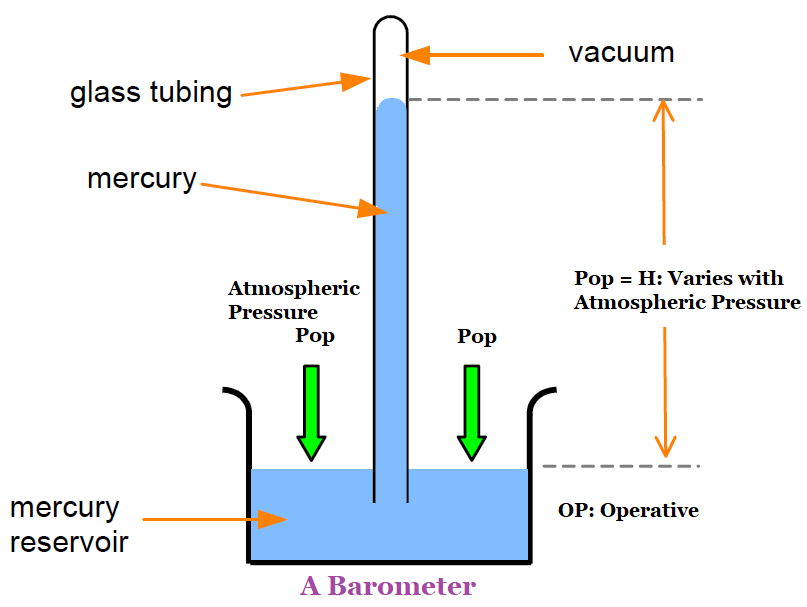
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure (atmospheric pressure) in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. The atmospheric pressure (ambient pressure) causes the fluid inside the tube to rise. So the barometer pressure is the atmospheric pressure which is known as Operative pressure in the Fluent software.
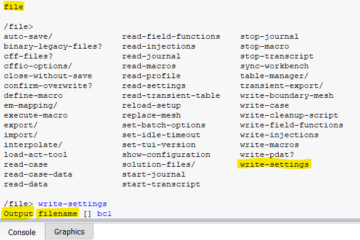
It is defined in the operation condition panel inside Ansys Fluent and the operating pressure menu.
Static pressure is the pressure at any point in the fluid. This pressure is a function of the state of the fluid, which for an ideal gas, is related to the density/volume of the fluid through the ideal gas law. It can be measured using an aneroid, piezometer etc.
A piezometer is either a device used to measure liquid pressure in a system by measuring the height to which a column of the liquid rises against gravity or a device that measures the pressure (more precisely, the piezometric head) of groundwater at a specific point. A piezometer is designed to measure static pressures and thus differs from a pitot tube by not being pointed into the fluid flow.
The concepts of dynamic and total pressure arise from Bernoulli’s equation for incompressible flows. Dynamic pressure is the pressure associated with the motion of the fluid and is directly proportional to the density and square of the velocity of the fluid. Total or stagnation pressure is defined as the sum of static and dynamic pressure.
A pitot tube, also known as a pitot probe, is a flow measurement device used to measure fluid flow velocity. The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the fluid flow. As this tube contains fluid, a pressure can be measured; the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure.
Stagnation (Total) pressure = static pressure + dynamic pressure
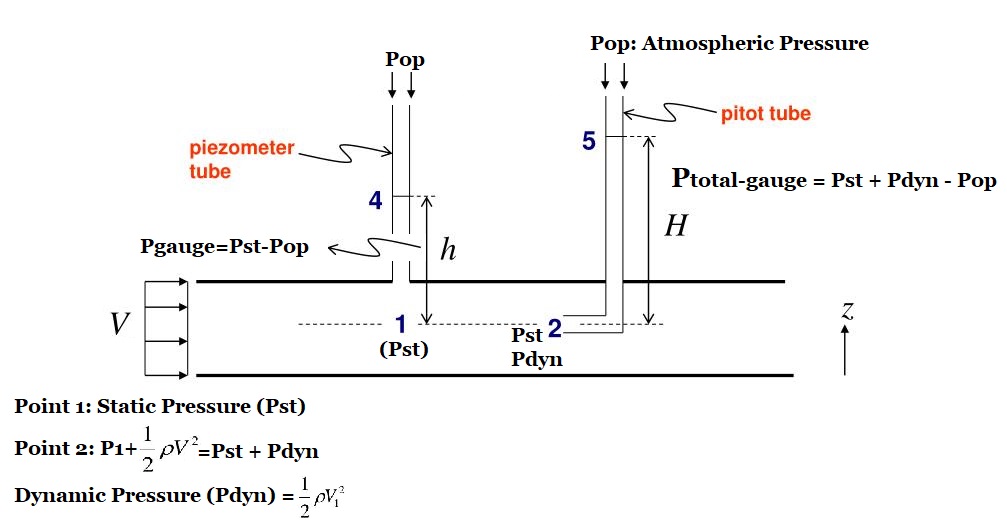
Pressure is an absolutely measurable quantity and therefore may be referred to as ‘absolute pressure’ when the reference point of measurement is equal to zero.
In Fluent, for problems where the variation in pressure is small compared to the mean value of absolute pressure, it is advisable to choose the reference point to be equal to the mean absolute pressure to minimize numerical errors. This reference point is referred to as the ‘operating pressure’ and may be specified in Fluent in the Operating Conditions panel accessed from Define->Operating Conditions.
The difference between absolute pressure and operating pressure is referred to as the ‘gauge pressure’. All pressure values reported in Fluent are gauge pressures.
This tutorial was prepared by XAV experts.
0 Comments