What is Cavitation?
Cavitation happens when vapor bubbles form in a liquid because flow dynamics cause the local static pressure to drop below the vapor pressure. Without accurate prediction of cavitation, users cannot effectively optimize designs and set operating parameters and limits, potentially exposing their products to unexpected vibration and damage.
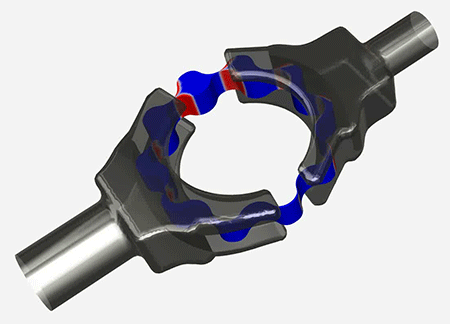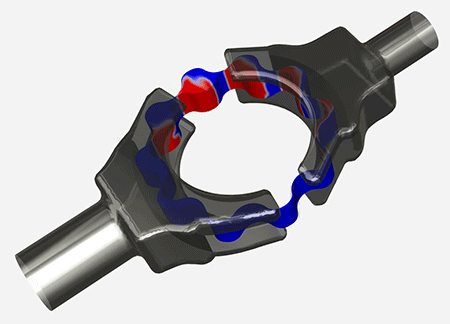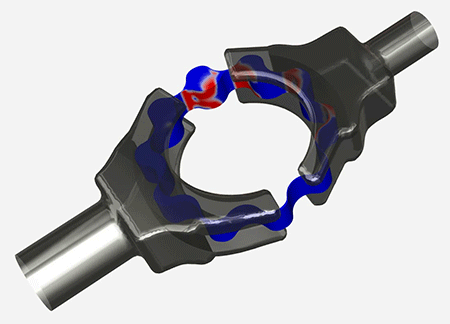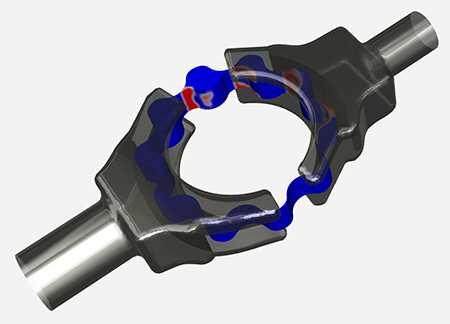
The phenomenon known as cavitation is the formation of vapor bubbles within a liquid when flow dynamics cause the local static pressure to drop below the vapor pressure. The bubbles usually last a short time, collapsing when they encounter higher pressure. This can cause noise and vibration, structural wear and damage, leading to reduced performance.
Cavitation can create problems within products that are related to fluid flow including:
- Pumps (positive displacement)
- Fuel injectors
- Valves
- Compressors
- Turbochargers
- Propellers (and other marine applications)
- Spillways
- Squeeze Film Dampers (SFDs)
However, it can also be useful in controlled applications:
- Ultrasonic devices (shock wave lithotripsy)
- Cavitation jets for cleaning surfaces
- Low drag torpedoes and marine hulls
Identifying the phenomenon early in the design process allows designs to be created without rework. However, it is usually impossible to identify cavitation during physical testing until it reaches high levels and the resulting noise and vibration become apparent. Even then, it is hard to confirm that it is the root cause of the problem. Many computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software packages have difficulty in predicting cavitation because they are not able to account for the motion of structural components; are not able to couple flow analysis with other physics, which is often needed for accurate simulation; and offer either a limited selection, or no selection of models. Without accurate prediction, users cannot effectively optimize designs and set operating parameters and limits — potentially exposing their products to unexpected vibration and damage.
Accurate simulation can enable your engineering team to quickly evaluate alternative product and process designs to increase efficiency, reliability, safety and durability in a competitive, time-critical environment. ANSYS CFD solutions provide the building blocks needed to accurately and quickly analyze cavitation. ANSYS dynamic or moving mesh capabilities make it easy to accurately model moving elements such as impellers or vanes that are commonly found in applications where the phenomenon is a concern. With ANSYS CFD solutions, you can easily predict interactions between fluids and structures, which is an important characteristic of many of these applications. Finally, ANSYS provides the most accurate multiphase modeling, including numerous choices of cavitation and turbulence submodels that maximize accuracy by matching the model to the application for the best fit.
In short, cavitation is the formation of vapor bubbles within a liquid when flow dynamics cause the local static pressure to drop below the vapor pressure. The bubbles usually last a short time, collapsing when they encounter higher pressure. Cavitation can cause noise and vibration, structural wear and damage, leading to reduced performance. It is a common problem in pumps (especially centrifugal or positive displacement pumps), compressors, hydraulic turbines, propellers, fuel injectors and other fluid devices subjected to high variations in pressure.
0 Comments